
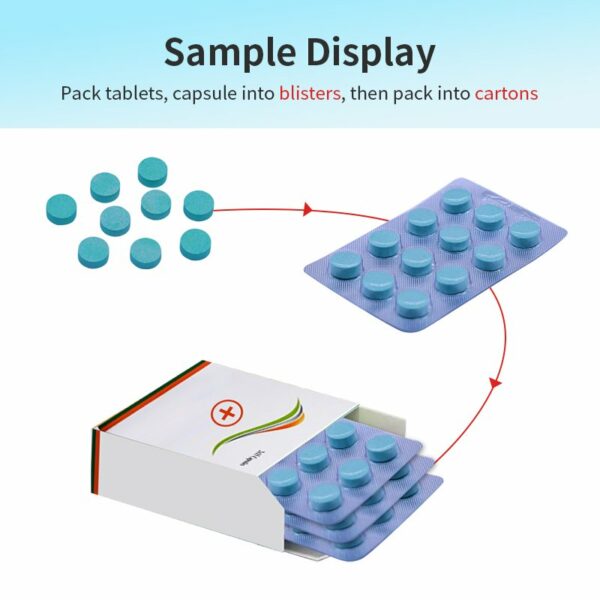








Linia pakująca w kartony typu blister
Linia pakująca w blistry automatyzuje proces end-to-end tworzenia opakowań typu blister i ładowania ich do kartonów. Najpierw PVC jest formowane termicznie w zagłębienia blistrowe. Produkty (tabletki, kapsułki) są precyzyjnie ładowane do tych blistrów za pomocą dostosowanych podajników. Następnie blister jest uszczelniany folią aluminiową za pomocą ciepła i ciśnienia, aby zapewnić ochronę przed manipulacją.
Zintegrowane systemy wizyjne sprawdzają wady, takie jak puste blistry, źle wyrównane uszczelki lub brakujące ulotki. Zatwierdzone blistry są następnie przenoszone do modułu kartonującego, gdzie wstępnie złożone pudełka są składane, wypełniane blistrami i wkładkami (instrukcjami) i zamykane za pomocą zakładek lub kleju. Mechanizmy odrzucające usuwają wadliwe jednostki, a gotowe kartony są wyprowadzane w celu etykietowania lub pakowania wtórnego.
Linia łączy formowanie blistrów, zamykanie, kontrolę i pakowanie w kartony w płynny, zgodny z cGMP przepływ pracy, zapewniając szybką produkcję, minimalną ilość odpadów i możliwość dostosowania do różnych rozmiarów produktów. Idealna do produktów farmaceutycznych, żywności i dóbr konsumpcyjnych, stawia na precyzję, higienę i skalowalność.
Specyfikacja:
Do 130 kartonów/min.
Dotyczy tabletek, kapsułek, pigułek itp.
3 lata gwarancji, 1 rok bezpłatnych części



