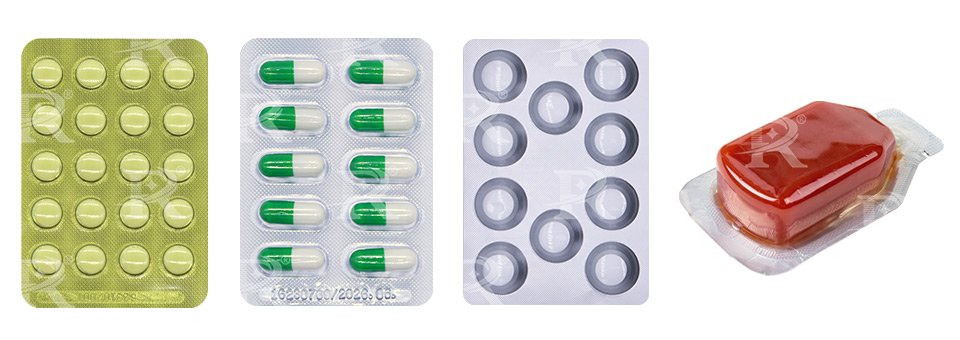
Blister packing machine is an important equipment in packaging. It can pack tablets, capsules, pills, candies, electronic cigarettes, soft capsules, big honey pills… It can also pack liquids such as ketchup, chocolate, honey, perfume, etc. It is an aluminum-pvc, aluminum-aluminum dual-purpose machine. Full servo drive, each station can be adjusted by hand wheel, convenient and fast, controlled by PLC programmable program.
Blister Packing Machine Working Principle
Blister packing machines are essential in the packaging industry, providing a secure and visually way to package various products. The working principle of a blister packing machine involves several key processes: forming, feeder, sealing, and cutting. Understanding each of these processes is crucial for optimizing the operation and maintenance of the machine. Here, we’ll delve into the detailed working principle of blister packing machines.
1. ایستگاه تشکیل
The first step in the blister packaging process is forming the blister cavities, which will hold the products. This step can be carried out through either thermoforming or cold forming. Generally, alu-pvc blisteres is formed by hot forming, and alu-alu blisters is formed by cold forming.
Thermoforming: In this process, a plastic film (usually PVC, PVDC, or PET) is fed into the machine and heated until it becomes pliable. The heated film is then molded into the desired cavity shape using a forming die. The die presses the heated film into the mold, creating the blister cavities.
Cold Forming: For products requiring better barrier properties, cold forming is used. In this method, a laminate of aluminum foil is fed into the machine and pressed into a mold using a forming die. This process does not involve heating and is typically used for products sensitive to moisture and oxygen.
2.Feeder Station
Once the blister are formed, the next step is filling these blisters with the product. This is usually done through an automatic feeding system that accurately places the product into each blisters. The filling process must be precise to ensure that each product fits correctly into its respective blisters without spillage or misalignment.
The feeding method can be selected according to the characteristics of the material. Brush feeders, guide feeders, and special feeders can be used.
Brush feeders are generally used for aluminum-plastic packaging, and the brush will not damage the material. It uses the brush to put the tablets or capsules into each blister. This feeding method is economical and practical.
Why are some materials packaged in aluminum-plastic packaging and some in aluminum-aluminum packaging? This is determined according to the characteristics of the product. Aluminum-aluminum packaging is for some materials that need to be stored away from light.
Guide feeders are generally used for aluminum-aluminum packaging. The brush feeding method will damage the surface of the aluminum foil and even scratch it. Therefore, guide feeders are selected for fast feeding speed.
There are also special feeders, which are expensive and are not recommended unless it is the characteristics of the material.
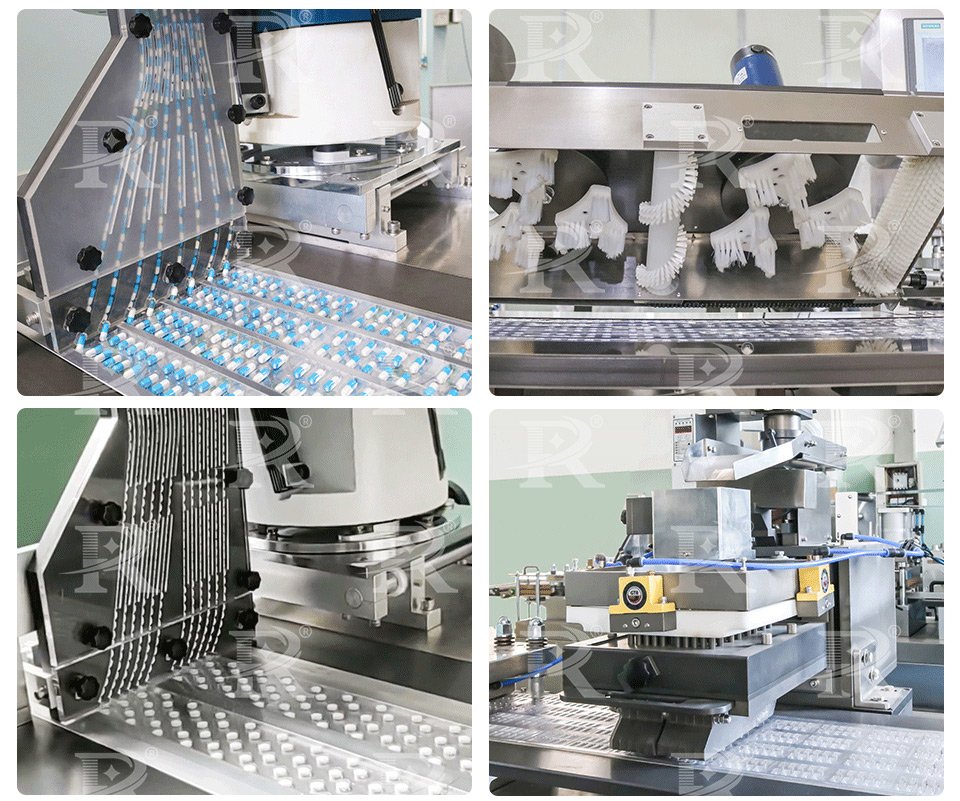

3.Heat Sealing Station
After the blisters are filled, the next step is heat sealing. Sealing material aluminum foil over the filled blisters and bonding it. The sealing process typically involves the following steps:
Heating: The alu foil and the edges of the plastic blisters are heated to a specific temperature.
Pressure Application: A sealing die applies pressure to bond the alu foil to the plastic film, creating a secure. This ensures the product is protected from external elements such as moisture, light, and air.
4.Cutting Station
The final step in the blister packing process is cutting. The sealed blister packs are cut into individual units or strips. This step involves:
Perforation: Creating perforations between individual blister packs if they need to be separated easily.
Cutting Die: A cutting die cuts the sealed sheet into the desired shapes and sizes, producing the final blister packs ready for packaging and distribution.
The working principle of a blister packing machine is a systematic process that ensures products are securely packaged in a visually appealing and protective manner. By understanding the intricacies of forming, filling, sealing, and cutting, operators can optimize the machine’s performance, ensuring efficient and high-quality blister packaging.
انواع ماشین آلات بسته بندی تاول زده
Blister packing machines are integral to various industries, providing efficient and secure packaging solutions. Different types of blister packing machines cater to specific packaging needs, depending on the product requirements, production volume, and material properties. Here, we will discuss the primary types of blister packing machines:
1.Flat plate blister packing machines
Flat plate blister packing machines are a type of blister packaging equipment that is highly versatile and commonly used in various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals, food, and consumer goods. These machines are known for their precision, ease of operation, and suitability for small to medium-scale production.
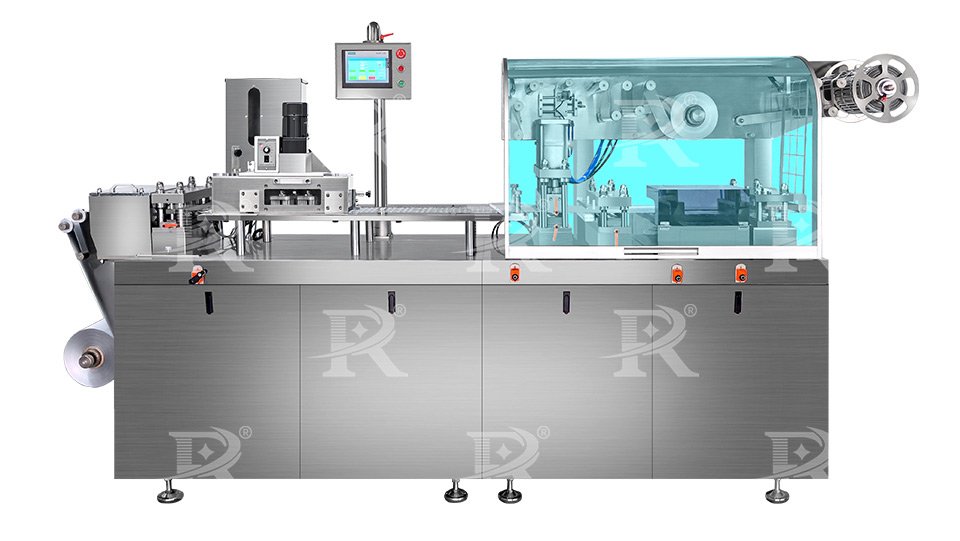
ویژگیهای کلیدی:
Precision Forming and Sealing: The flat plate design ensures accurate and consistent forming and sealing of blister packs.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, food items, and small consumer goods.
Ease of Operation: Typically user-friendly with straightforward controls, making them accessible for operators with varying levels of expertise.
Customization: Can be customized to handle different blister pack sizes and configurations.
Compact Design: Often more compact than rotary or roller-type machines, making them suitable for smaller production environments.
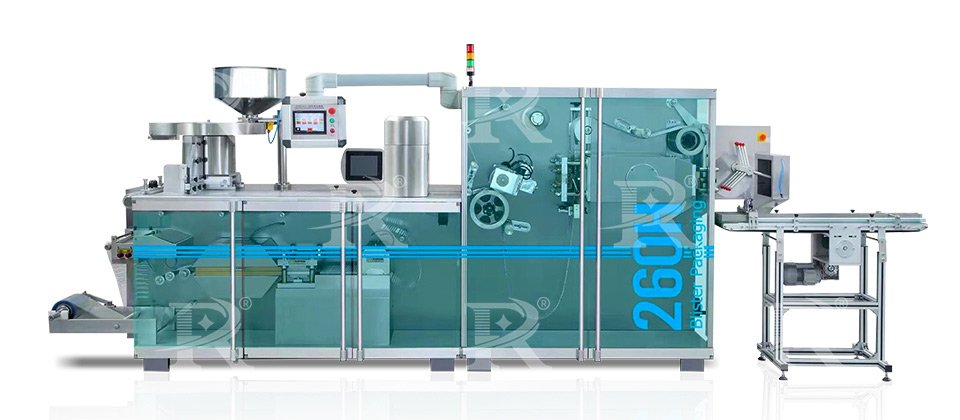
2.Roller-Type Blister Packing Machines
Roller-type blister packing machines are designed for high-speed, continuous production. These machines are well-suited for large-scale manufacturing environments where efficiency and throughput are critical.

ویژگیهای کلیدی:
Continuous Feed: Uses continuous rolls of plastic film and sealing material.
High-Speed Operation: Capable of producing a high volume of blister packs per minute.
Precision: Ensures accurate forming, filling, and sealing at high speeds.
Applications: Commonly used in large-scale pharmaceutical and consumer goods production.
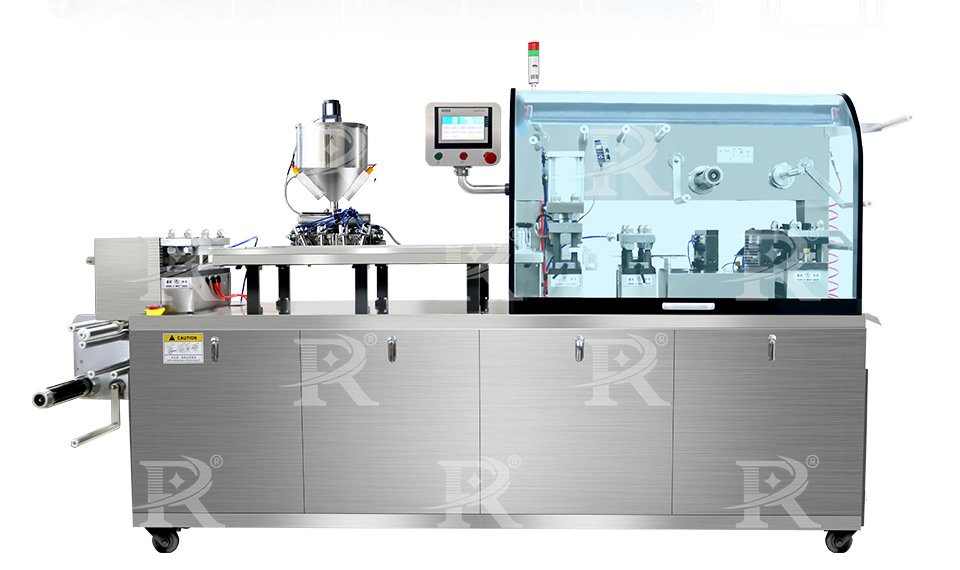
3.Liquid Blister Packing Machine
Liquid blister packing machines are specialized equipment designed for packaging liquid or semi-liquid products into blister packs. These machines provide a secure, tamper-evident, and convenient packaging solution, ideal for a range of industries including pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and chemicals. This guide will delve into the working principle, features, and applications of liquid blister packing machines.

ویژگیهای کلیدی:
Precision Filling: Advanced dosing systems ensure accurate filling of each blister cavity, essential for liquid products.
Airtight Sealing: Ensures the liquid product is securely enclosed, preventing leakage and contamination.
Versatile Forming Materials: Can handle a variety of forming and lidding materials suitable for different types of liquid products.
Automated Operation: Many machines feature automated controls for efficient and consistent operation, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Hygienic Design: Made from materials that are easy to clean and sterilize, ensuring compliance with hygiene standards.
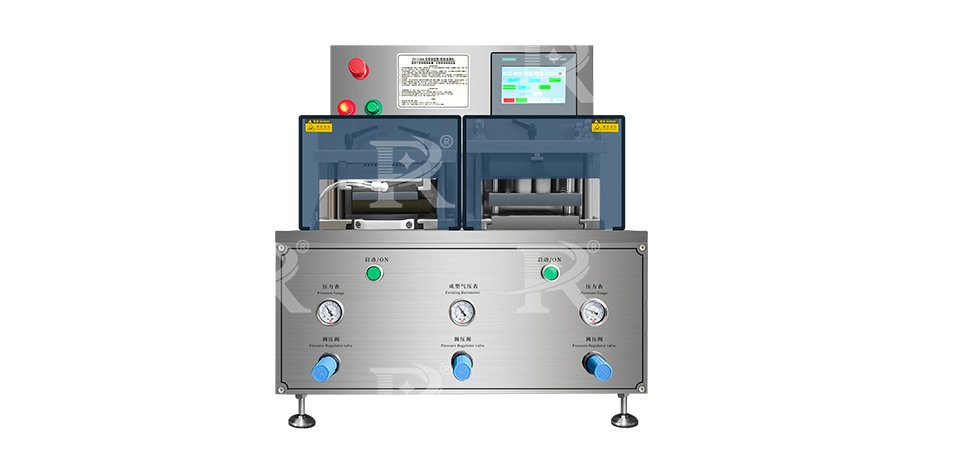
4.Laboratory Blister Packing Machines
Laboratory blister packing machines are designed for small-scale production or laboratory use. These machines are compact, easy to operate, and cost-effective, making them suitable for small batches and custom packaging.

ویژگیهای کلیدی:
Compact Size: Small footprint, suitable for limited space environments.
Manual or Semi-Automatic Operation: Often involves manual loading and sealing processes.
Flexibility: Suitable for packaging a wide range of small products.
Applications: Used in laboratories, small-scale production, and custom packaging.
The type of blister packing machine chosen depends on the specific requirements of the product, production volume, and desired packaging properties. Whether for high-speed large-scale production or small-batch custom packaging, there is a blister packing machine tailored to meet those needs. Understanding the differences and capabilities of each type ensures the selection of the most appropriate machine for efficient and effective packaging operations.
Applications of Blister Packing Machines
1.Pharmaceutical Industry
Tablets and Capsules: Blister packs provide a secure and hygienic way to package tablets and capsules, protecting them from moisture, light, and contamination.
Oral Thin Films and Powders: Specialized blister packs are used for dissolvable films and powdered medications.
Unit Dose Packaging: Ensures accurate dosing and tamper-evident packaging for individual doses, improving patient compliance and safety.
2.Food and Beverage Industry
Condiments and Sauces: Blister packs are ideal for single-serving portions of condiments like ketchup, mustard, and salad dressings.
Snacks and Confectionery: Packaging of small candies, chewing gum, and chocolate pieces.
Liquid Foods: Packaging of liquid food items like honey, syrup, and nutritional supplements in single-use packs.
3.Medical Devices
Syringes and Needles: Sterile and secure packaging for single-use medical devices.
Diagnostic Kits: Blister packs for test strips and other components of diagnostic kits.
Surgical Instruments: Packaging of small surgical instruments and tools.
4.Cosmetics Industry
Creams and Gels: Single-use packs for creams, gels, and lotions.
Makeup and Fragrance Samples: Blister packs for sampling products like perfumes, foundation, and other cosmetics.
Blister packing machine serve a crucial role across various industries by providing secure, efficient, and convenient packaging solutions. Their ability to protect products, ensure accurate dosing, and enhance consumer convenience makes them indispensable in pharmaceutical, food, consumer goods, medical, cosmetic, and chemical applications. By choosing the appropriate blister packing machine, businesses can significantly improve product safety, shelf life, and user experience, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.


