What Is The Count Bottle Filling Line
Count bottle filling line is an automated production line used in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries to accurately count and fill products, such as tablets, capsules, gummies or soft gels, into bottles.
What Does The Count Bottle Filling Line Consist Of
Count bottle filling line include: bottle unscrambler, lifting feeder, tablet capsule counting machine, checkweigher, desiccant inserter, capping machine, aluminum foil sealing machine, labeling machine. The machine how to working?
Αποκρυπτογράφος μπουκαλιών
Αποκρυπτογράφος μπουκαλιών is a machine designed to automatically orient and position bottles correctly on capsule counting line. The working principle of a bottle unscrambler typically involves the following steps:
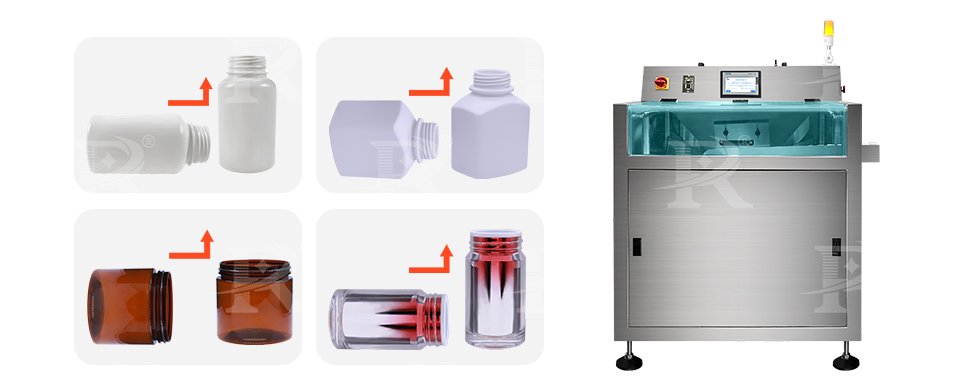
Bottle Loading: Empty bottles are loaded into a bulk hopper or feeder, often in a random orientation.
Sorting Mechanism: The bottles are transferred from the hopper to a rotating disk, where they are sorted and guided into specific channels. This mechanism uses gravity, centrifugal force, or vibration to move the bottles toward the next stage.
Orientation and Alignment: As the bottles move through the channels, they are guided into an upright position by rails, guides, or funnels. Misaligned bottles are either corrected or returned to the bulk hopper for another pass through the system.
Detection and Adjustment: Sensors or mechanical detectors ensure that only correctly oriented bottles pass through. Any bottles that are not correctly aligned are redirected back to the sorting stage.
Discharge and Transfer: Once the bottles are properly oriented, they are released onto a conveyor belt in a single file, ready to be filled or processed further down the production line.
Speed Control: The unscrambler operates at adjustable speeds to match the pace of the downstream filling and packaging processes, ensuring a continuous flow of bottles.
Lifting Feeder Machine
Lifting feeder is a machine used to elevate and feed materials, such as tablets, capsules, gummies or other small items, from a lower level to a higher position on a production line. The working principle of a lifting feeder generally involves the following steps:

Material Loading: Materials(tablets, capsules, gummies or other small items) are loaded into a hopper or feed tray at the base of the lifting feeder. This is typically done manually or automatically from a previous stage in the production process.
Conveying Mechanism: The lifting feeder uses a conveying mechanism, such as a belt, bucket, or vibratory system, to move the materials upwards. In a bucket conveyor, for example, the materials are collected in small buckets attached to a belt or chain, which rotates to lift the materials to the desired height.
Lifting and Elevation: As the conveying mechanism operates, it lifts the materials from the hopper to a higher level. The speed and angle of elevation can usually be adjusted to control the flow rate and match the needs of the downstream equipment
Discharge: At the top of the lift, the materials are discharged from the conveyor into a receiving hopper, chute, or directly onto count bottling machine.
Return and Refill: The conveying mechanism returns to the starting position, ready to pick up more materials from the hopper and repeat the process.
Control System: The lifting feeder is typically equipped with sensors and a control system that monitors the material level in the hopper and adjusts the feeding rate to ensure a continuous and consistent supply.
Tablet Capsule Counting Machine
Tablet capsule counting machine can count 3-40mm tablets, capsules, gummies into bottles. The working principle of a count bottling machine involves the following steps:

Feeding: Tablets or capsules are fed into the machine from a hopper or feeder. The products are typically directed onto a vibrating plate or conveyor that evenly distributes them.
Product Orientation and Separation: The products are spread out and aligned on the conveyor or vibrating plate. They are guided into single-file lines, ensuring that each item is separated for accurate counting.
Counting Mechanism: The machine uses sensors, usually optical or infrared, to count each item as it passes through a designated point. These sensors detect and record each product, ensuring an accurate count before it is dispensed into the bottle.
Bottle Positioning: Empty bottles are fed onto the conveyor and positioned under the dispensing chute. The machine ensures that each bottle is correctly aligned to receive the counted products.
Filling Process: Once the correct number of products is counted, they are dispensed into the bottle. The machine controls the flow to ensure that only the precise number of items is filled into each bottle.
Checkweigher Machine
Checkweigher is a machine used in production lines to ensure that the weight of packaged products meets specified standards. The working principle of a checkweigher involves the following steps:

Product Feeding: After the count bottling machine completes the counting, the bottles pass through the conveyor belt and enter the checkweigher machine. The conveyor moves the products at a consistent speed.
Weighing Mechanism: As each bottles passes over the weighing platform or scale integrated into the conveyor belt, the checkweigher measures its weight. This is typically done using a high-precision load cell, which converts the weight into an electrical signal for processing.
Data Processing: The checkweigher’s control system compares the measured weight of each product with the preset weight limits. These limits define the acceptable weight range (e.g., minimum and maximum allowable weights).
Sorting or Rejection: If the product’s weight falls within the acceptable range, it continues along the conveyor to desiccant Inserter. If the product is underweight or overweight, it is automatically diverted to a rejection area by pusher.
Feedback and Adjustment: The checkweigher can provide real-time feedback to the count bottle filling line, enabling adjustments to be made to the filling or packaging process if weight inconsistencies are detected. This helps maintain consistent product quality and reduces waste.
Data Recording and Reporting: The checkweigher often records the weight data and generates reports for quality control purposes. This data can be used to monitor production trends, ensure compliance with regulations, and optimize the production process.
Desiccant Inserter Machine
Desiccant inserter machine is used to automatically insert desiccant packets into bottles or containers, typically in the pharmaceutical, food, or packaging industries, to keep the contents dry and moisture-free. The working principle of a desiccant inserter machine involves the following steps:

Desiccant Supply: Desiccant packets are loaded into a feeding system, usually a hopper or magazine, where they are stored and fed into the machine.
Separation and Orientation: The desiccant packets are separated from the bulk supply and oriented for insertion. This is often done using a vibrating or rotary mechanism that ensures each packet is individually fed into the insertion system.
Bottle or Container Positioning: The bottles is conveyed into position under the desiccant insertion point. A sensor or positioning system ensures that each container is correctly aligned and ready to receive the desiccant packet.
Insertion Mechanism: Dropped into the bottle or container. The timing of this insertion is synchronized with the movement of the bottles on the conveyor to ensure precise operation.
Continuous Operation: The machine operates continuously, automatically inserting desiccant packets into containers as they pass through the line, ensuring that the packaging process is efficient and consistent.
Μηχανή κάλυψης
Capping machine is designed to automatically place and secure caps onto bottles or containers as part of a production line. The working principle of a capping machine involves the following steps:

Bottle Feeding: Bottles is fed onto a conveyor belt and moved towards the capping station. The machine ensures that the bottles are correctly spaced and oriented for capping.
Cap Sorting and Feeding: Caps are loaded into a cap feeder or sorter, which organizes and aligns them. The caps are then fed into a chute or track that guides them to the capping head. This ensures that the caps are correctly oriented before being placed onto the bottles.
Cap Placement: As each bottle passes under the capping head, a cap is picked up and placed onto the bottle’s opening.
Capping Mechanism: The capping machine then tightens or secures the cap onto the bottle. Different types of capping mechanisms can be used, depending on the type of cap and bottle:
Screw Capping: The machine applies rotational force to screw the cap onto the bottle, ensuring it is tight and secure.
Snap Capping: For snap-on caps, the machine applies downward pressure to snap the cap into place.
Crimp Capping: For crimp-style caps, the machine uses a crimping tool to seal the cap onto the bottle neck.
Torque Control: In screw capping machines, the torque applied to the cap can be precisely controlled to ensure the cap is neither too loose nor too tight. This is important for maintaining product integrity and ensuring consumer safety.
Quality Control and Verification: Some machines include sensors or vision systems to verify that each cap is correctly placed and secured. If a cap is missing, improperly placed, or not tightened to the correct specification, the bottle can be automatically rejected or sent for re-capping.
Aluminum Foil Sealing Machine
Aluminum foil sealing machine is used to seal containers with an aluminum foil layer, creating an airtight and tamper-evident seal. This is commonly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. The working principle of an aluminum foil sealing machine involves the following steps:

Container Feeding: Containers is fed onto a conveyor belt and moved towards the sealing station. The machine ensures that each container is correctly positioned for sealing.
Cap with Aluminum Foil: The containers typically have caps with an aluminum foil liner inside. The cap is placed on the container, with the aluminum foil positioned over the container’s opening.
Induction Heating: The container passes under an induction coil, which generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field. This field induces an electric current in the aluminum foil, causing it to heat up.
Heat Transfer: The heat generated in the aluminum foil melts the heat-sensitive polymer coating on the underside of the foil. This polymer layer bonds with the rim of the container, forming a seal.
Pressure Application (optional): In some machines, a pressure pad or mechanism may be used to press the foil firmly against the container’s opening during heating, ensuring a uniform and secure seal.
Cooling and Solidification: After the heating process, the polymer cools and solidifies, creating an airtight and tamper-evident seal between the aluminum foil and the container. The container is then released from the sealing station.
Quality Control and Verification: The sealed containers may pass through a quality control station, where sensors or cameras check the integrity of the seal. Any containers with faulty seals can be automatically rejected.
Μηχανή επισήμανσης
Labeling machine is used to automatically apply labels to bottles. Labeling machines are widely used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and packaging. The working principle of a labeling machine involves the following steps:

Product Feeding: Bottles are fed onto a conveyor belt that moves them towards the labeling station. The machine ensures that each item is correctly spaced and oriented for accurate label application.
Label Feeding: Labels are supplied in a roll or sheet format and are fed into the labeling machine. The machine unrolls the labels and positions them for application. A sensor detects the start of each label to ensure precise placement.
Label Detection and Alignment: Sensors or markers on the label web detect the position of each label, ensuring that the labels are aligned properly before being applied. The labels are peeled off the backing material as they reach the application point.
Label Application: As the product passes through the labeling station, the machine applies the label to the product’s surface. Depending on the type of labeling machine, different methods are used:
Wrap-Around Labeling: The label is wrapped around cylindrical or round products, such as bottles or cans. The product may rotate during application to ensure full coverage.
Front and Back Labeling: Separate labels are applied to the front and back surfaces of the product. The machine precisely positions each label on the correct side.
Top or Bottom Labeling: Labels are applied to the top or bottom surfaces of flat products or containers.
Corner or Edge Labeling: For packages or boxes, labels may be applied to corners or edges, wrapping around two adjacent surfaces.
Pressure Application: A roller or brush may apply gentle pressure to ensure that the label adheres smoothly and securely to the product’s surface without wrinkles or bubbles.
Sensor and Control System: The machine uses sensors to monitor the labeling process, ensuring that each label is applied correctly and at the right speed. The control system can adjust the speed, position, and alignment of the labels to match different product sizes and shapes.
Inspection and Quality Control: After labeling, the product may pass through an inspection station where sensors or cameras check the placement, alignment, and adhesion of the labels. Any products with misapplied or missing labels can be rejected or sent for re-labeling.
Whether it is single machine or whole capsule counting filling line, ruidapacking can provide complete services.


