1. Introdução
Tablet or capsule, which one is better? Choosing between capsules and tablets is a primary consideration for medications and supplements. This article explores the key differences, pros and cons, and factors to consider when determining which is better suited for your needs.
2. Capsule vs Tablet: What Are Capsules and Tablets?
Tablets and capsules are the two key types of oral medication and nutritional supplements. They are mostly serving the same purpose for curing diseases, improving health condition, etc. But what are these two forms of pills in specific?
1) What Are Cápsulas?
Pill capsules are made of gelatin or vegetarian materials in the form of cylindrical or oval-shaped containers. They contain either liquid, powder, or granules and are designed to dissolve quickly in the digestive system. Gel capsules come in two primary forms:
- Hard gelatin capsules: These are made of two pieces that fit together and are commonly used for powdered or granulated substances.
- Soft gelatin capsules (Softgels): These are one-piece capsules used for oils and liquid-based medications, as well as softgel multivitamins, etc

2) What Are Comprimidos?
Tablet pills are solid, compressed doses of medication or supplements generally manufactured by tablet press machines. They can be coated by film coating machine or uncoated as the way it is, and their ingredients are usually held together with binding agents such as microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and cellulose derivatives. There are different types of medication tablets, including:
- Conventional Tablets: Cost-effective, stable, fast absorption, may have poor taste and be fragile.
- Coated Tablets: Easier to swallow, protects drug stability, more expensive and heavier.
- Effervescent Tablets: Fast dissolution in water, easier to swallow, moisture-sensitive and high sodium content.
- Chewable Tablets: Convenient, better taste for children; may require sweeteners and cause tooth sensitivity.
- Buccal & Sublingual Tablets: Rapid absorption, bypasses stomach,limited to specific drugs and can irritate the mouth.
- Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODT): Fast dissolution without water, convenient for children, more expensive and moisture-sensitive.
- Sustained-Release Tablets: Prolonged effect, fewer doses, complex production and risk of dose dumping.
3. Tablet vs Capsule: What’s the Difference?
1) Cápsulas vs Tablets: Processo de fabricação
Capsule and tablet productions involve several key steps to ensure the quality and performance of the final product. Here is a brief overview of the process and pharmaceutical machinery used from material processing to final product treatment.
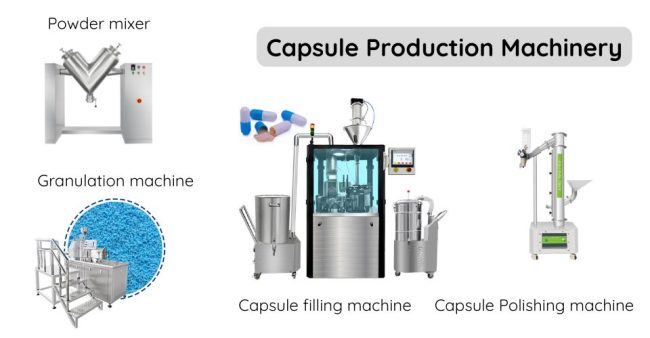
Cápsula Filling Manufacturing
- Material Preparation: Purchase or manufactureempty pill capsules (gelatin or vegetarian-based), as well as preparing the raw materials in the form of granules, powders, pellets, etc. Power mixers and granulation machines may be used to optimize material consistency in some cases.
- Cápsula Filling: Once the materials are ready, load them into the hoppers of a capsule filling machine. Both semi-automatic and fully automatic capsule fillers can ensure efficient and high-quality capsule production.
- Final Capsule Polishing (Optional): Use a capsule polishing machine to remove residual powder from the capsule surface, enhancing the final product’s quality and appearance.
Tablet Pressing Produção
- Tablet Compression: Load the prepared materials into the hopper of a tablet press machine. A automatic rotary tablet presses can be used to compress the materials into uniform tablets with precise weight and hardness.
- Tablet Coating (Optional): If a coated tablet is required, transfer the compressed tablets to a tablet coating machine. This process enhances tablet stability, taste, and appearance using film or sugar coating techniques.
- Final Tablet Polishing & Dedusting: Use a tablet deduster and polishing machine to remove excess powder and sharp edges, ensuring a smooth surface and high-quality finish before packaging.

2) Cápsula vs Tablet: Sizes Differences
Capsules and tablets come in various sizes, which impact ease of swallowing and dosage control. Capsule sizes range from size 000 (largest) to size 5 (smallest). For a better understanding, here below is a capsule size chart: |
|||
| Cápsula Size | Capsule Volume (ml) | Body Length (mm) | Body Diameter (mm) |
| 000 | 1.37 | 25.70 | 9.44-9.54 |
| 00 | 0.95 | 23.40 | 8.15-8.25 |
| 0 | 0.68 | 21.70 | 7.30-7.40 |
| 1 | 0.50 | 19.30 | 6.61-6.69 |
| 2 | 0.37 | 17.80 | 6.05-6.13 |
| 3 | 0.30 | 15.70 | 5.55-5.61 |
| 4 | 0.21 | 14.20 | 5.00-5.08 |
| 5 | 0.13 | 11.10 | 4.50-4.91 |
Tablets do not have a standardized sizing system like capsules. The tablet sizes depend on the amount of active ingredients and binding agents they contain. Tablets are often scored to allow splitting for dose adjustments.
 | ||
| Tablet Size | Diameter | Common Use |
| Small | 5mm – 8mm | Low-dose medications, vitamins, supplements. |
| Padrão | 8mm – 12mm | Regular-dose medications, common supplements. |
| Large | 12mm – 20mm | High-dose medications, tablets with larger quantities of active ingredients. |
| Extra Large | 20mm – 25mm | Tablets for very high doses or those with multiple active ingredients. |
3) Tablet vs Capsule: Absorption Differences
When it comes to the questions of capsule vs tablet absorption, capsule pills dissolve quickly in the stomach as their gelatin or vegetarian shells break down rapidly, releasing the active ingredients for fast absorption. Softgel capsules, which contain liquid medication, generally have higher bioavailability, making them more effective. Additionally, capsules medications are gentler on the stomach since they don’t require as many binders or fillers.
Tablets take longer to absorb because they are compressed solids that need to break down before the drug is released. However, they can be designed for controlled release, such as enteric-coated or extended-release tablets, which delay absorption to target specific areas in the digestive system. While standard tablets may have lower bioavailability, advanced formulations improve effectiveness.
4) Tablets vs Capsules: Prós e contras
In order to get a general understanding, here is a table for the key differences between tablets versus capsules, or advantages and disadvantages of tablets and capsules.
| Recurso | Cápsulas | Comprimidos |
| Absorption | Pro: Faster absorption, especially liquid-filled. | Con: Slower absorption, controlled release possible. |
| Custo | Con: More expensive. | Pro: More cost-effective. |
| Manufacturing | Requires capsule filling equipment | Tablet press machine. |
| Shelf Stability | Con: Sensitive to moisture. | Pro: More stable. |
| Customization | Con: Limited to certain materials. | Pro: More flexibility in shape and size. |
| Ease of Swallowing | Pro: Easier due to smooth texture | Con: Can be harder to swallow. |
| Taste and Smell | Pro: Tasteless, masks unpleasant flavors. | Con: May have a noticeable taste or odor. |
5. Cápsulas vs Tablets: Which is Better for Pharma Production?
Many people ask the question that, “are capsule better than tablets?” “Tablets or capsules which one is better?” When choosing between pill vs capsule, several factors must be considered, including material compatibility, cost considerations, and market preferences. Below is a detailed comparison of tablets versus capsules:
1) Material Compatibility
- Capsules: If your medications contain liquid or oil-based formulations or substances sensitive to compression, capsules are a better form to create this type of pills. They offer better protection for certain active ingredients and can mask unpleasant tastes or odors.
- Tablets: If your pills require efficient incorporation of large quantities of active ingredients, then the tablet form medication is an ideal choice. They can also enable various release profiles, such as extended or immediate release.
2) Medication Cost Consideration
- Capsules: If your production budget allows for higher raw material costs and specialized capsule filling equipment, capsules may be a suitable choice. However, keep in mind that softgel capsules require even more advanced encapsulation technology, increasing overall production expenses.
- Tablets: If your goal is to minimize production costs, tablet pills are the more budget-friendly option. Their manufacturing process is faster and more efficient, making them ideal for large-scale pharmaceutical and supplement production.
3) Market Evaluation
- Capsules: If your target consumers prioritize ease of swallowing and prefer tasteless or odor-free medication, capsules are a better option. Research found that 66% of supplement users favor two-piece capsules due to their smooth texture and ability to mask strong odors or tastes.
- Tablets: If your focus is on pharmaceutical drug production, tablets are the preferred choice. They dominate the market due to their cost-effectiveness, long shelf life, and ability to accommodate various drug release modifications.
6. What Tablet or Capsule Manufacturing Equipment Should You Choose?
Selecting the appropriate pharmaceutical equipment is crucial for guaranteeing consistency, efficiency, and high-quality production. The choice of pharmaceutical machinery depends on the specific requirements of capsule or tablet manufacturing. Below is an overview of essential manufacturing equipment for each type of production:
Para Cápsulas:
- Capsule filling machines efficiently fill capsules with powders, granules, or liquids. The automated production can adopt semi-automaticencapsulation machines or fully automatic capsule fillers which are able to enhance production efficiency and accuracy.
- Softgel encapsulation machines are specialized for producing liquid-filled softgel capsules, ensuring precise dosage and high-quality sealing.
Para Comprimidos
- Granulation equipment ensures uniform powder mixture before tablet compression, improving tablet consistency, hardness, and dissolution properties.
- Máquinas de prensagem de comprimidos compress granulated materials into tablet form, with rotary tablet pressing models and high speed tablet press machine designed for different production capacities.
- Tabletfilme coating machines apply protective or functional coatings to tablets, enhancing stability, appearance, and controlled drug release.
7. Pharmaceutical Eequipamento Manufacturer Recommendation
After learning the differences between tablets and capsules, as well as some knowledge about the related tablet capsule manufacturing equipment, you may have a clear idea which form of medication and which machines to use for your pills production. Next step is to choose reliable pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment from a trusted supplier. Among the top pharmaceutical machinery manufacturers in the industry, Ruidapacking stands out to be a recommended choice.
In specific to the manufacturing of tablet and capsule, here below are two major machines as a reference.
| Recurso | Cápsula Filling Machine | Tablet Press Machine |
| Modelo | NJP1500D | ZP26/40 D |
| Picture |  |
 |
| Capacidade | 90,000 pcs/hour | 260,000 pcs/hour |
| Especificação | – Capsule Size: #000, 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 – Filling Rage: Power, granules, pellets, tablets. | – Max Diameter: 25mm – Max Pressure: 100 kN – Pre-pressing: 20 kN |
| Features | – Internal groove cam. – High dosing accuracy of ≤3%. – Modular design, fast mold change in 15 minutes. | – Single-piece waste rejection. – Pressure real time monitoring. – Residual powder recycling. |
| Suitable Buyer | High speed high accuracy pharmaceutical or supplement manufacturers for capsule filling. | Mass production and high precision high performance tablet manufacturers. |
8. Conclusão
Choosing between capsules or tablets ultimately depends on various factors. Knowing these differences will help you to make informed choices regarding pharmaceutical and supplement production. While choosing the key pharmaceutical equipment manufacturers, Ruidapacking stands out as a reputable supplier, recognized globally for its high-quality machines and exceptional service.


