Il confezionamento efficace delle capsule è fondamentale per garantire la sicurezza del prodotto, la conformità e la soddisfazione dei clienti. Che si tratti di industria farmaceutica, nutraceutica o di integratori, il modo in cui si confezionano le capsule può avere un impatto sulla durata di conservazione, sull'usabilità e sull'attrattiva del mercato. Questa guida definitiva vi guiderà attraverso le fasi e le considerazioni essenziali per il confezionamento delle capsule, aiutandovi a ottimizzare il vostro processo e a fornire un prodotto di alta qualità.

1. Comprendere i requisiti di confezionamento delle capsule
- 1.1. Conformità normativa
- Il confezionamento delle capsule non è solo una questione di estetica, ma anche di rispetto di rigorosi standard normativi. A seconda del settore, potrebbe essere necessario rispettare le normative FDA, GMP o ISO. Ad esempio, le capsule farmaceutiche spesso richiedono un imballaggio a prova di bambino per evitare l'ingestione accidentale. Assicuratevi sempre che il vostro imballaggio soddisfi i requisiti legali necessari per evitare multe o richiami.
- 1.2. Protezione del prodotto
- Le capsule sono sensibili a fattori ambientali come umidità, luce e ossigeno. Un imballaggio adeguato garantisce che rimangano efficaci e sicure per il consumo. I materiali di barriera, come la pellicola o le plastiche specializzate, possono proteggere le capsule dalla degradazione e dalla contaminazione, prolungandone la durata di conservazione.
2. Scegliere i materiali di imballaggio giusti
La scelta del giusto materiale di confezionamento è una delle fasi più critiche del processo di confezionamento delle capsule. Il materiale scelto determinerà la protezione delle capsule, la facilità d'uso della confezione e persino la percezione del prodotto da parte dei consumatori. Di seguito analizzeremo le opzioni di confezionamento più comuni e i loro pro e contro.
2.1. Bottiglie e barattoli
Le bottiglie e i barattoli sono tra le scelte più popolari per il confezionamento delle capsule, soprattutto per i prodotti sfusi come gli integratori alimentari.
- Pro:
- Efficiente dal punto di vista dei costi: Le bottiglie sono generalmente poco costose da produrre e sono quindi ideali per le aziende che vogliono ridurre al minimo i costi.
- Facilità d'uso: Sono semplici da riempire, sigillare ed etichettare e richiedono un'attrezzatura specializzata minima.
- Versatilità: Disponibili in varie dimensioni, forme e materiali (ad esempio, plastica o vetro), i flaconi possono ospitare quantità e tipi diversi di capsule.
- Riutilizzabilità: Molte bottiglie sono dotate di tappi richiudibili, che consentono ai consumatori di riutilizzarle per altri scopi.
- Contro:
- Protezione limitata: Sebbene le bottiglie proteggano le capsule dai danni fisici, potrebbero non offrire sufficienti proprietà di barriera contro l'umidità o l'ossigeno, a meno che non siano abbinate a essiccanti o a rivestimenti specializzati.
- Ingombro: Le bottiglie possono occupare più spazio sugli scaffali rispetto ad altre opzioni di confezionamento, con conseguente aumento dei costi di spedizione e stoccaggio.
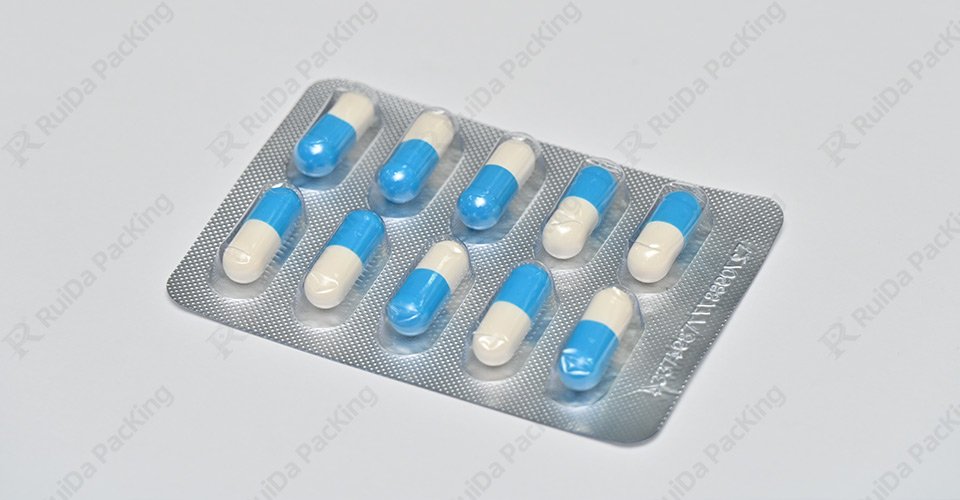
2.2. Confezioni blister
I blister sono un'opzione di confezionamento di qualità superiore, spesso utilizzata per prodotti farmaceutici o integratori di alto valore.
- Pro:
- Protezione superiore: I blister offrono eccellenti proprietà barriera, proteggendo le capsule da umidità, luce e contaminazione. Ogni capsula è sigillata singolarmente, per garantire la massima protezione.
- Evidente la manomissione: Le confezioni in blister sono a prova di manomissione e danno ai consumatori la certezza della sicurezza del prodotto.
- Portabilità: Il loro design compatto li rende facili da trasportare, ideali per chi è sempre in movimento.
- Precisione di dosaggio: Ogni scomparto del blister può essere progettato per contenere una dose specifica, riducendo il rischio di sovradosaggio o sottodosaggio.
- Contro:
- Costo più elevato: La produzione di blister è più costosa a causa dei materiali e dei macchinari necessari.
- Produzione complessa: Il processo di creazione dei blister è più laborioso e richiede attrezzature specializzate.
2.3. Sacchetti e bustine
Le buste e le bustine sono confezioni leggere e flessibili, spesso utilizzate per prodotti monodose o da viaggio.
- Pro:
- Leggero e compatto: Le buste occupano uno spazio minimo, riducendo i costi di spedizione e stoccaggio.
- Personalizzabile: Possono essere progettati in varie forme e dimensioni, con possibilità di cerniere richiudibili o di nodi a strappo.
- Economico per piccole quantità: Ideali per prodotti monodose o campioni, le buste sono un'opzione conveniente per il confezionamento su piccola scala.
- Contro:
- Durata limitata: Le buste sono meno robuste dei flaconi o dei blister e potrebbero non fornire una protezione adeguata per la conservazione a lungo termine.
- Problemi ambientali: Molte buste sono realizzate con materiali non riciclabili, che potrebbero non essere in linea con gli obiettivi di sostenibilità.
Tabella di confronto: Materiali da imballaggio
Tipo di imballaggio | Livello di protezione | Costo | Ideale per |
Bottiglie/barattoli | Moderare | Basso | Imballaggio alla rinfusa, stoccaggio a lungo termine |
Confezioni blister | Alto | Medio | Prodotti monodose ad alto valore aggiunto |
Buste/Sacchetti | Da basso a moderato | Basso | Prodotti monouso e on-the-go |
3. Progettazione di un imballaggio efficace per le capsule
- 3.1. Requisiti per l'etichettatura
- La confezione deve contenere informazioni essenziali come il nome del prodotto, le istruzioni per il dosaggio, la data di scadenza e il numero di lotto. Assicuratevi che le etichette siano chiare, leggibili e conformi alle normative del settore.
- 3.2. Branding ed estetica
- L'imballaggio è spesso il primo punto di contatto tra il prodotto e il consumatore. Utilizzate design accattivanti, colori vivaci e il logo del vostro marchio per creare un'impressione memorabile.
- 3.3. Caratteristiche di facile utilizzo
- Incorporate caratteristiche come tappi facili da aprire, buste richiudibili o nodi a strappo per migliorare l'esperienza dell'utente. Questi piccoli dettagli possono avere un impatto significativo sulla soddisfazione dei clienti.
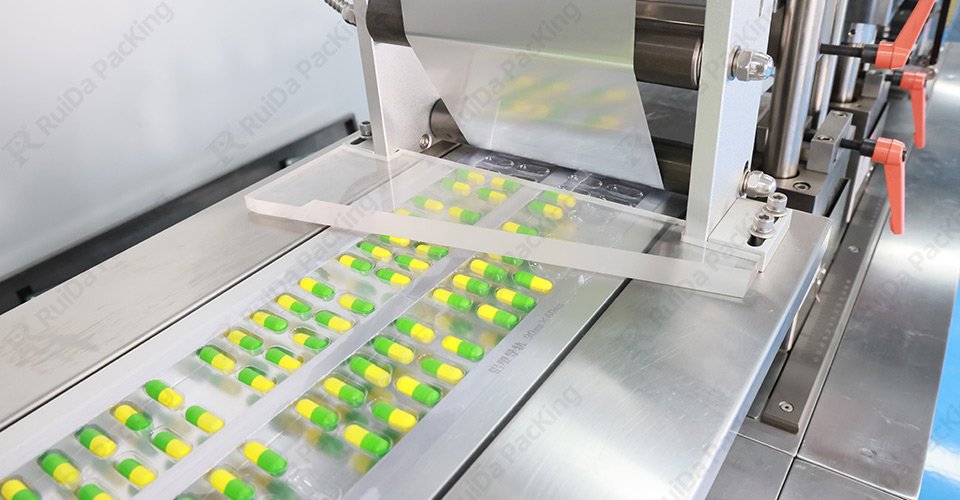
4. Apparecchiature di confezionamento e automazione
- 4.1. Confezionamento manuale e automatico
- Il confezionamento manuale è adatto a operazioni su piccola scala, ma può richiedere molto tempo ed essere soggetto a errori. I sistemi automatizzati, pur essendo più costosi all'inizio, offrono maggiore efficienza e coerenza.
- 4.2. Apparecchiature chiave per il confezionamento di capsule
- Le macchine per il riempimento e la tappatura delle bottiglie, le macchine per il confezionamento di blister e le macchine per la sigillatura delle buste sono essenziali per ottimizzare il processo di confezionamento.
- 4.3. Manutenzione e calibrazione
- La manutenzione e la calibrazione regolari delle apparecchiature assicurano prestazioni costanti e prevengono costosi tempi di inattività.

5. Controllo qualità e test
- 5.1. Test di tenuta
- Assicuratevi che l'imballaggio sia ermetico per evitare la contaminazione e l'ingresso di umidità.
- 5.2. Test di stabilità
- Eseguite dei test per valutare come il vostro imballaggio protegge le capsule in varie condizioni ambientali, come la temperatura e l'umidità.
- 5.3. Test di prova della manomissione
- Verificate che le vostre confezioni soddisfino gli standard di antimanomissione per garantire la sicurezza dei consumatori.
6. Considerazioni sullo stoccaggio e sul trasporto
- 6.1. Fattori ambientali
- Le capsule sono sensibili alla temperatura, all'umidità e alla luce. Conservatele in un luogo fresco e asciutto per preservarne la qualità.
- 6.2. Imballaggio per la spedizione
- Utilizzate un imballaggio esterno robusto e materiali di imbottitura per proteggere le capsule durante il trasporto. Considerate l'utilizzo di imballaggi isolati per i prodotti sensibili alla temperatura.
Conclusione
Confezionamento di capsule richiede una pianificazione accurata, i materiali giusti e un'attenzione particolare alla qualità. Seguendo questa guida definitiva, potrete assicurarvi che le vostre capsule siano protette, conformi e pronte a stupire i vostri clienti. Ricordate che un ottimo packaging non solo protegge il vostro prodotto, ma migliora anche la reputazione del vostro marchio.