1. المقدمة
أصبحت الأقراص المغلفة معويًا عنصرًا أساسيًا في التركيبات الصيدلانية الحديثة، وخاصةً للأدوية التي تتطلب تجاوز البيئة الحمضية للمعدة. ولإنتاج أقراص مغلفة معويًا، تلعب المعدات الصيدلانية، وخاصةً آلات طلاء الأقراص، دورًا محوريًا. في هذا الدليل، سنستكشف ماهية الأقراص المغلفة معويًا، وكيفية عملها، وأنواع طرق الطلاء المستخدمة في صناعة الأدوية، والآلات اللازمة لإنتاجها.

2. ما هو الطلاء المعوي؟
الغلاف المعوي هو طبقة واقية تُوضع على الأقراص أو الكبسولات أو الأقراص المغلفة، تمنعها من الذوبان في البيئة الحمضية للمعدة. بل يضمن هذا الغلاف مرور الدواء عبر المعدة سليمًا، ويذوب فقط في البيئة الأكثر اعتدالًا أو قلويةً للأمعاء.
عادةً ما يُصنع الغلاف المعوي من بوليمرات حساسة لدرجة الحموضة (pH)، حيث تبقى ثابتة في درجات الحموضة المنخفضة (الحمضية)، ولكنها تتحلل عند مستويات pH أعلى (عادةً ما تكون أعلى من pH 5.5 إلى 7.0)، والتي توجد في الأمعاء الدقيقة. يُعد الغلاف المعوي مفيدًا بشكل خاص في:
• حماية المكونات النشطة الحساسة للأحماض
• منع تهيج المعدة الناتج عن بعض الأدوية
• استهداف إطلاق الدواء إلى الأمعاء لتحسين الامتصاص أو التأثير العلاجي

3. كيف تعمل الأقراص المغلفة معويًا؟
تعمل الأقراص المغلفة معويًا باستخدام طبقة خارجية متخصصة تقاوم حموضة المعدة، لكنها تذوب في حموضة الأمعاء المتعادلة أو القلوية. إليك كيفية عمل هذه العملية خطوة بخطوة:
- الابتلاع: بمجرد ابتلاع القرص، فإنه ينتقل عبر المريء إلى المعدة.
- مقاومة الأحماض: تظل الطبقة المعوية سليمة في المعدة (درجة الحموضة 1.0-3.5)، مما يحمي المكونات النشطة من الانطلاق أو التحلل بواسطة حمض المعدة.
- العبور إلى الأمعاء: ينتقل القرص إلى الأمعاء الدقيقة، حيث يرتفع الرقم الهيدروجيني تدريجيًا إلى حوالي 6.5-7.5.
- إذابة الطلاء: تم تصميم الطلاء المعوي ليذوب عند درجة الحموضة العالية هذه، مما يسمح للقرص بالتفكك وإطلاق المكون الدوائي النشط (API).
- الامتصاص المستهدف: يتم بعد ذلك امتصاص الدواء في الأمعاء، إما للعلاج الموضعي (على سبيل المثال، الأدوية المضادة للالتهابات لأمراض الأمعاء) أو للدورة الدموية الجهازية.
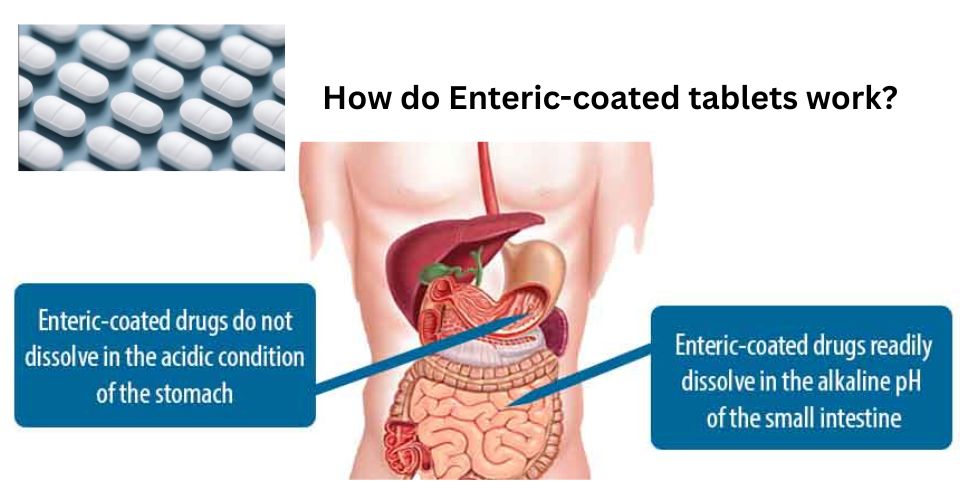
(حقوق الصورة: https://www.pharmapproach.com/enteric-coating-2/)
4. أمثلة على الأدوية والعقاقير المغلفة معويًا
تُستخدم الأقراص المغلفة معويًا على نطاق واسع في الأدوية الموصوفة طبيًا والمتاحة بدون وصفة طبية. في الصناعات الدوائية والغذائية، يُستخدم الطلاء المعوي على مجموعة متنوعة من أشكال الجرعات، بما في ذلك الأقراص المغلفة معويًا والكبسولات المغلفة معويًا. يوفر كل شكل فوائد مختلفة حسب أهداف التركيبة ونوع الدواء وتفضيلات التصنيع.
مغلفة معوية شائعة المخدرات
فيما يلي بعض أمثلة الأقراص المغلفة المعوية للأدوية المغلفة المعوية المستخدمة بشكل شائع لفئات مختلفة وأسباب مختلفة.
حبوب ل | فئة | لماذا تستخدم الطلاء المعوي؟ |
حمض المعدة | مثبط مضخة البروتون | يحمي الأدوية الحساسة للأحماض، ويعزز الامتصاص في الأمعاء |
المعدة | مضاد للالتهابات/مضادات الالتهاب غير الستيرويدية | يقلل من تهيج المعدة، ويستخدم لصحة القلب |
مسكن للألم | تسكين الألم/مضادات الالتهاب غير الستيرويدية | يؤخر الإطلاق لمنع قرحة المعدة |
البروبيوتيك | مكملات صحة الأمعاء | تحمي البروبيوتيك المغلفة معويًا الثقافات الحية من خلال حمض المعدة |
الهضم | العلاج بالإنزيمات الهضمية | يفرز إنزيمات في الاثني عشر للهضم |
تتوفر أيضًا أقراص مغلفة معويًا بأشكال مختلفة، مثل الأقراص أو الكبسولات. فيما يلي جدول لمقارنة هذين النوعين من الأدوية المغلفة معويًا.
ميزة | أقراص مغلفة معوية | أقراص مغلفة معوية |
شكل | مستديرة أو بيضاوية | مستطيل، انسيابي |
سهولة البلع | معتدل | أسهل من الأجهزة اللوحية |
تطبيق الطلاء | يتم تطبيقه عن طريق آلات طلاء الفيلم أو المقلاة | نفس الأجهزة اللوحية |
موقع الذوبان | الأمعاء (المحفزة بالرقم الهيدروجيني) | الأمعاء |
الاستخدام النموذجي | الأدوية الموصوفة والمكملات الغذائية | الفيتامينات المتعددة والأدوية التي لا تستلزم وصفة طبية |
تفضيلات التصنيع | فعّالة من حيث التكلفة، وحجم كبير | سهولة التعامل، غبار أقل |
5. إيجابيات وسلبيات الأقراص المغلفة معويًا
تُستخدم الأقراص المغلفة معويًا على نطاق واسع في صناعة الأدوية لقدرتها على توصيل المكونات الفعالة بأمان وفعالية. ومع ذلك، في حين أنها يمد إنها تتميز بمزايا كبيرة، ولكنها تأتي أيضًا مع بعض التحديات المتعلقة بالإنتاج والصياغة.

1) مزايا المغلفة المعوية حبوب
- الحماية من حمض المعدة
طلاء معوي يكون مُصممة لتبقى سليمة في البيئة الحمضية للمعدة، ولا تذوب إلا عند وصولها إلى درجة الحموضة العالية للأمعاء الدقيقة. هذا مثالي للأدوية التي يُمكن أن تُعطّل أو تُهيّج بحمض المعدة. - تحسين راحة المريض
قد تُهيّج الأدوية، مثل مضادات الالتهاب غير الستيرويدية، بطانة المعدة. يُساعد الغلاف المعوي على تقليل الآثار الجانبية المعدية المعوية، مما يُحسّن التزام المريض بالعلاج. - إطلاق الدواء المستهدف
تتيح هذه الطلاءات توصيل الدواء إلى موقع محدد، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية للأدوية التي تعمل محليًا في الأمعاء أو تحتاج إلى إطلاق متأخر لأسباب علاجية. - إخفاء الطعم
بعض المواد الفعالة كيميائيًا لها طعم مر أو غير مستساغ. تساعد الأغطية المعوية على إخفاء هذا الطعم بمنع ذوبانه في الفم أو المعدة.
2) عيوب الأقراص المغلفة معويًا
- التصنيع المعقد عملية
يتطلب تطبيق الطلاء المعوي التحكم الدقيق في مواد الطلاء ودرجة الحرارة ومعدلات الرش ومعايير التجفيف، وغالبًا ما يتطلب آلات طلاء أقراص متخصصة. - وقت إنتاج أطول
بالمقارنة مع الأقراص المغلفة بغشاء، تستغرق الأدوية المغلفة معويًا وقتًا أطول لإنتاجها بسبب خطوات الطبقات المتعددة ودورات التجفيف التي يتم التحكم فيها. - خطر عدم اكتمال الطلاء
إذا كانت عملية الطلاء غير متسقة أو كانت إعدادات الجهاز معطلة، فقد يذوب القرص جزئيًا في المعدة، مما يفشل الغرض منه. - حساسية التخزين
بعض البوليمرات المعوية حساسة للرطوبة ودرجة الحرارة، مما يتطلب ظروف تعبئة وتخزين دقيقة للحفاظ على سلامة الطلاء.
6. الطلاء المعوي مقابل الطلاء الغشائي مقابل الطلاء السكري: ما هو الفرق؟
في إنتاج الأقراص الصيدلانية هناك ثلاث طرق رئيسية لطلاء الأقراص وهي الطلاء المعوي والفيلمي والسكر، فما هي الاختلافات بينها؟
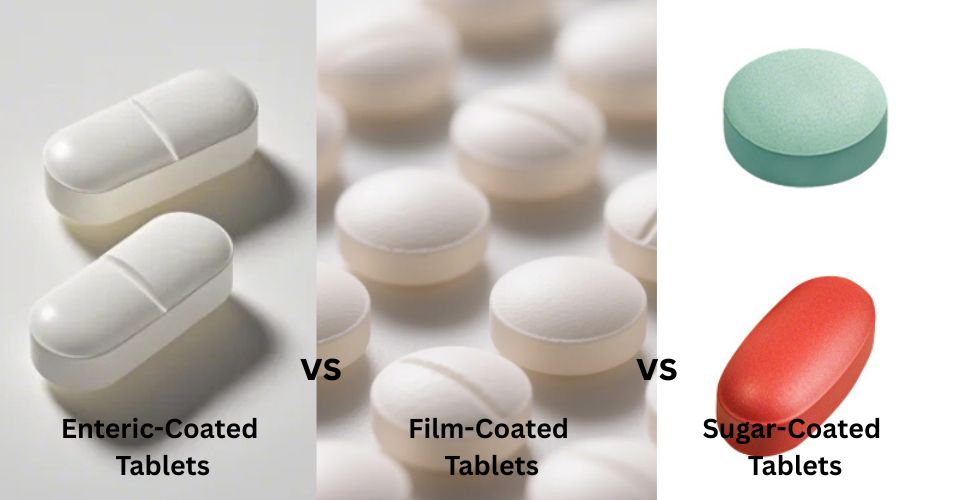
1) الاختلافات بين التعريف والتطبيق
- الطلاء المعوي هو طلاء حساس لدرجة الحموضة (pH)، يسمح للأقراص بتجاوز المعدة والذوبان في الأمعاء. يُستخدم عادةً مع الأدوية الحساسة للحموضة أو لتخفيف تهيج المعدة.
- طلاء الفيلم طبقة رقيقة من البوليمر تُوضع على الأقراص لحمايتها من الرطوبة، أو لإخفاء الطعم، أو لتحسين مظهرها. تُستخدم على نطاق واسع في الأدوية والمكملات الغذائية لفعاليتها.
- طلاء السكر طريقة تقليدية تستخدم طبقات من السكر لإضفاء لمسة نهائية ناعمة ولامعة. تُحسّن هذه الطريقة المذاق والمظهر، لكنها تستغرق وقتًا أطول في الإنتاج وتزيد وزن الأقراص بشكل ملحوظ.
2) المعوي مقابل الغشاء مقابل طلاء السكر: الاختلافات الرئيسية
ميزة | الطلاء المعوي | طلاء الفيلم | طلاء السكر |
موقع الإصدار | الأمعاء | المعدة أو الإصدار المعدل | معدة |
سمك الطلاء | واسطة | رفيع | سميك |
إخفاء الطعم | معتدل | جيد | ممتاز |
سرعة الإنتاج | معتدل | سريع | بطيئ |
حماية من الرطوبة | عالي | عالي | قليل |
المظهر المرئي | وظيفية | ملون أو شفاف | لامع، زخرفي |
حالة الاستخدام | إطلاق متأخر، حماية من الأحماض | الأجهزة اللوحية القياسية والعلامات التجارية | أقراص قابلة للمضغ، للأطفال، عشبية |
3) المعوي مقابل الغشاء مقابل طلاء السكر: المعدات وعملية الطلاء
تعتمد جميع الطلاءات الثلاثة على آلات طلاء الأقراص، ولكن المعلمات والمدة تختلف كثيرا:
- عملية طلاء الأمعاء
يتطلب تحكمًا دقيقًا في رش البوليمر الحساس لدرجة الحموضة، ودرجة حرارة التجفيف، ومراحل الطلاء المتعددة. يُستخدم عادةً أحواض طلاء مثقبة أو طلاءات طبقة سائلة. - عملية طلاء الفيلم
أسرع وأكثر كفاءة. تُرشّ الأقراص بمحلول بوليمري وتُجفّف في وعاء طلاء تحت تدفق هواء ودرجة حرارة مُتحكّم بهما. - عملية طلاء السكر
طريقة تستغرق وقتًا طويلاً وتتضمن وضع طبقات متعددة من الشراب والألوان والمواد المانعة للتسرب باستخدام قوالب طلاء تقليدية. قد يستغرق إكمالها ساعات.
7. المعدات الصيدلانية الرئيسية لطلاء الأقراص
يتطلب طلاء الأقراص المعوي معدات صيدلانية، مثل آلات طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية، لضمان توزيع هذه الطبقة المعوية بالتساوي والفعالية، وهو أمر أساسي لفعالية الأقراص وسلامة المرضى. فيما يلي الأنواع الرئيسية من المعدات الصيدلانية المستخدمة في طلاء الأقراص، وخاصةً في الإنتاج الصناعي.
1) آلات طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية
تُعدّ آلات طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية ركيزةً أساسيةً لإنتاج الأدوية على نطاق واسع. فهي تستخدم أنظمة رش متطورة، وأدوات تحكم قابلة للبرمجة، وأنظمة إدارة درجة الحرارة لتطبيق طلاءات موحدة بكفاءة. تُقلل هذه الآلات بشكل كبير من تباين الطلاء، وتُقلل من هدر المنتج، وتُحسّن الإنتاجية التشغيلية، مما يجعلها مثاليةً للإنتاج الضخم للأقراص المغلفة معويًا والمغلفة بغشاء.
آلة طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية الموصى بها: RD-BG-80
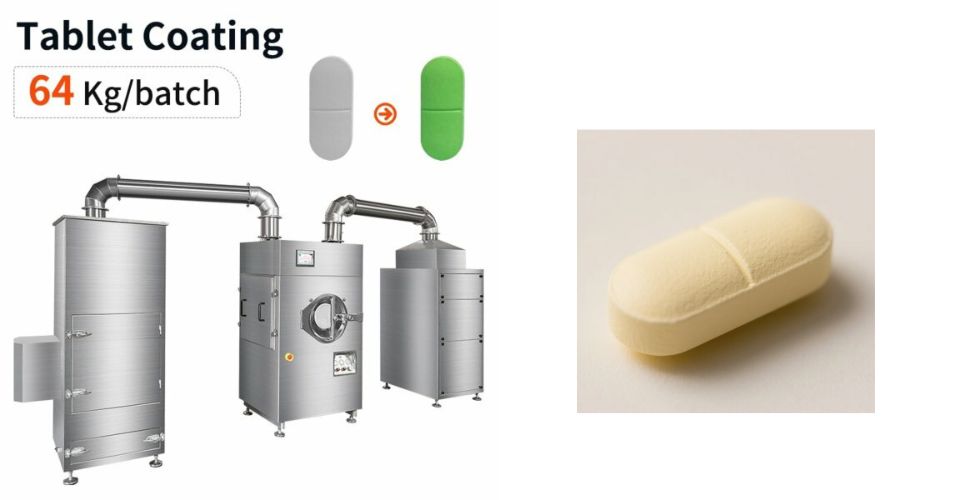

(حقوق الصورة: www.ruidapacking.com)
بالمقارنة مع النماذج الأخرى من آلة طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية، فإن هذا النموذج لديه المزايا والميزات الرئيسية على النحو التالي:
- نظام رش ايواتا, الدقة والاتساق: تستخدم العديد من آلات الطلاء الموجودة في السوق فوهات الرش الأساسية، ولكن RD-BY-80 تستخدم فوهات Iwata عالية الجودة، والمعروفة بالذرات الدقيقة والتغطية المتسقة، مما يقلل من هدر مواد الطلاء وإعادة العمل.
- تنوع في أنواع الطلاء المتعددة: تم تحسين بعض النماذج فقط لطلاء الفيلم أو طلاء السكر، ولكن هذا النموذج يتعامل مع الفيلم والسكر والطلاء المعوي بشكل جيد على حد سواء، مما يوفر المرونة لخطوط المنتجات المختلفة.
- كفاءة التجفيف المتقدمة: يضمن استخدام أسطوانة مثقبة مع نظام هواء ساخن متكامل تجفيفًا أسرع وأكثر انتظامًا من المقالي الناعمة القياسية، مما يقلل من وقت المعالجة ويحسن جودة الطلاء.
2) طلاءات المقلاة المثقبة
طلاءات المقلاة المثقبة تُستخدم على نطاق واسع في طلاء الأغشية، وطلاء السكر، والطلاء المعوي. تُحمَّل الأقراص في أسطوانة مثقبة تدور مع دوران الهواء الساخن عبر الثقوب. يُرش محلول الطلاء على الأقراص المتقلِّبة، ويُجفِّف الهواء الدافئ كل طبقة بسرعة. تضمن هذه الطريقة تغطية متساوية وتحافظ على سلامة الأقراص طوال العملية.
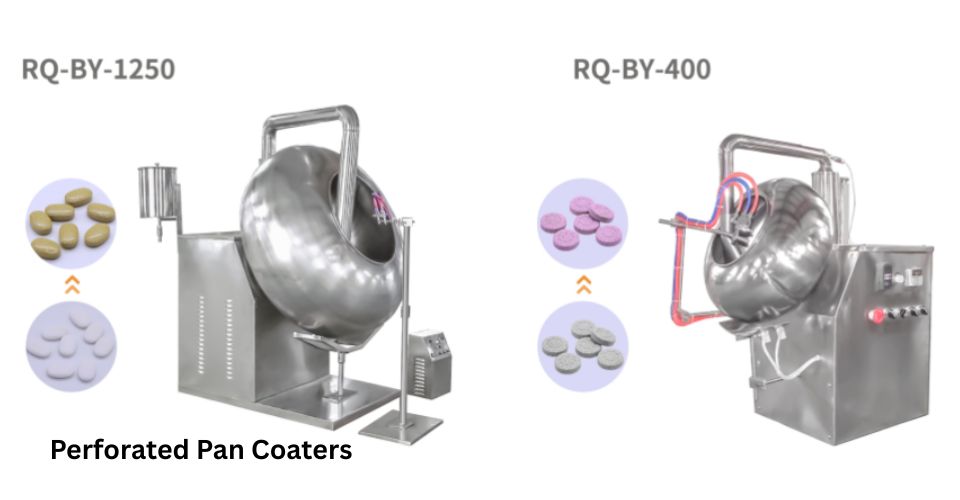

(حقوق الصورة: www.richpacking020.com)
3) طلاءات السرير السائل
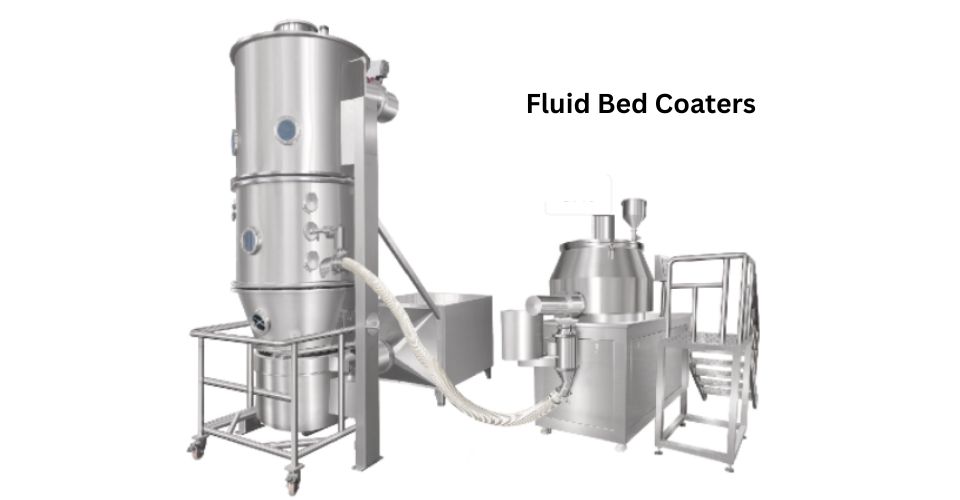
تُخصص آلات طلاء الطبقة المميعة لطلاء الأقراص الصغيرة والحبيبات والكريات. في هذا النظام، تُعلق الجسيمات في تيار هواء صاعد، بينما تُرشّ مادة الطلاء من الأسفل. توفر هذه التقنية تجانسًا ممتازًا في الطلاء، وهي مفيدة بشكل خاص للمنتجات التي تتطلب طبقات متعددة أو طلاءات وظيفية مثل الطلاء المتأخر أو الطلاء المستمر.

8. الأسئلة الشائعة/المشاكل الشائعة
غالبًا ما يواجه المصنّعون وفرق الصياغة تحدياتٍ رئيسيةً وأسئلةً متكررةً عند العمل مع الأقراص المغلفة معويًا. فيما يلي الأسئلة والمشاكل الأكثر شيوعًا من منظور الأعمال التجارية بين الشركات (B2B)، بالإضافة إلى الحلول ونصائح الخبراء.
س1: لماذا يتقشر الطلاء المعوي أو يتشقق أثناء الإنتاج؟
عادةً ما يشير التقشر أو التشقق إلى مشاكل في تركيبة الطلاء أو معايير التجفيف. قد يُسهم في ذلك تركيز البوليمر غير المناسب، أو الإجهاد الميكانيكي المفرط، أو عدم كفاية التجفيف.
حل:
- تحسين لزوجة محلول الطلاء ومحتوى المواد الصلبة.
- استخدم آلة طلاء الأقراص الأوتوماتيكية ذات التحكم الدقيق مع أنظمة الهواء الساخن.
- تجنب التحميل الزائد للأسطوانة والتقليل من تآكل الأقراص.
س2:كيفية ضمان سمك الطلاء المتناسق عبر جميع الأقراص؟
يمكن أن يؤدي الطلاء غير المتناسق إلى الذوبان المبكر أو فشل الإطلاق المتأخر.
حل:
- استخدم مسدسات الرش الآلية وأنظمة المراقبة في الوقت الفعلي على آلات الطلاء.
- تأكد من الحصول على حجم وشكل موحد للقرص من خلال مكبس أقراص دوار مع تحملات ضيقة.
س3: كيف يمكن تجنب التلوث المتبادل أثناء إنتاج الطلاء المعوي؟
يعد التلوث المتبادل بمثابة إشارة تحذيرية تنظيمية، وخاصة في المرافق متعددة المنتجات.
حل:
- استخدم المعدات ذات التصميم سريع التنظيف ومسارات المنتج المجزأة.
- تنفيذ الإجراءات التشغيلية القياسية (SOPs) لتنظيف الخطوط والتحقق منها باستخدام اختبارات المسحة.
س4: هل يمكن لآلات الطلاء المعوي التعامل مع أنواع متعددة من الطلاءات (الفيلم والسكر وما إلى ذلك)؟
نعم، ولكن فقط إذا كانت الماكينة تدعم ملفات تعريف الطلاء القابلة للبرمجة وفوهات الرش القابلة للتبديل.
حل:
- اختر طلاء أقراص متعدد الاستخدامات مع إمكانيات متعددة للعمليات.
- العمل مع شركات تصنيع المعدات الصيدلانية التي تقدم الاستشارات والتدريب على حلول طلاء الأقراص.
9. الخاتمة
تُوفّر الأقراص المغلفة معويًا توصيلًا مُركّزًا للدواء، وتحمي المكونات الحساسة من حمض المعدة. وهي أساسية للعديد من التركيبات الدوائية الحديثة. بالنسبة لمُصنّعي المنتجات الصيدلانية، يُعدّ فهم أنواع الطلاء واختيار المعدات الصيدلانية المناسبة، مثل آلات طلاء الأقراص، أمرًا أساسيًا لضمان جودة المنتج وامتثاله للمواصفات. مع توفر المعدات والمعرفة المناسبتين، يُصبح إنتاج الأقراص المغلفة معويًا عالية الأداء فعالًا وموثوقًا.


